Poker Hand Rankings - Texas Holdem Starting Hands Chart. Expected value is the average number of big blinds this hand will make or lose. For example: AA from the Small Blind in a $3/$6 game will make, on average, 2.71 times the big blind, or $16.20 per hand (2.71. $6). On the other hand, 22 from the Button (D or Dealer position), will make -$0.12 EV, or -$0.72 in a $3/$6 game (6.$0.12). As shown in the poker hand rankings chart, the order of poker rankings (from the highest to the lowest) is: Royal Flush, Straight Flush, Four-of-a-Kind, Full House, Flush, Straight. Relating the Top 10% Range to Your Online Play. The top ten percent of starting hands serves as a basic chart for profitable hole cards; however, the most important use of this list may be to assign specific ranges to your opponents’ tendencies. Once you know what ten-percent looks like, you will be able to recognize what 3% looks like and 20%.
- Ranking Best Starting Poker Hands To The Worst Poker Hands
- Rank Of Poker Hands
- Best Starting Poker Hands Hold'em
- Ranking Best Starting Poker Hands Texas Hold Em
- Poker Starting Hand Chart
One of hold’em’s most crucial decisions is, do I see the flop or don’t I see the flop? In this lesson we’ll examine the importance starting hand selection and what factors you need to consider before deciding whether to hold’em or fold’em.
There are 169 different two card starting hand combinations in hold’em poker. This number assumes, for the sake of argument, that is the same as , or any other suited combination. If you are not dealt a pair, then your starting hand will either be suited or unsuited, and either connected or unconnected (gapped). This means your starting hand will fall into one of the following five categories:
- Pairs – e.g. , ,
- Suited connectors – e.g. , ,
- Connecting cards – e.g. , ,
- Suited unconnected cards – e.g. , ,
- Unconnected cards – e.g. , ,
Unconnected cards might be one, two, three-gapped, or more. The bigger the gap, the less chance you have of hitting a straight. For example, if you hold 73, then you’d need a flop of 456 for the straight. But holding T8, you could flop a straight with 9JQ or 679.
The Best Starting Hands in Hold’em
Let’s start by talking about the best starting hands, which are often referred to as ‘premium hands’. There is some disagreement amongst poker players as to which starting hands are the best, but few would dispute the value of the first of our three main groups, Aces and Kings.
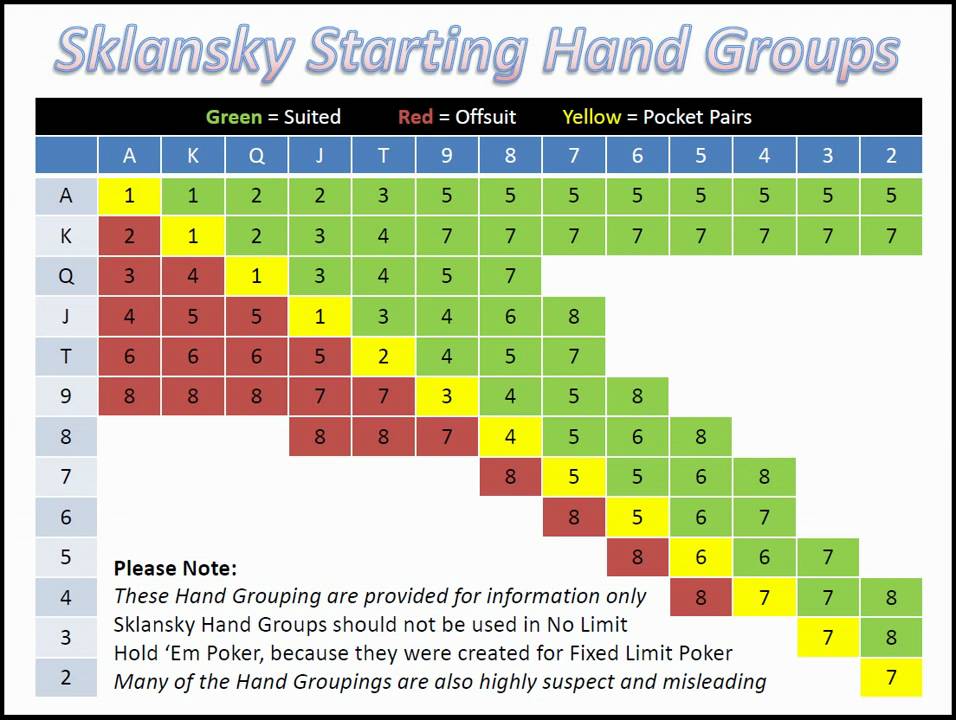
Group 1: AA, KK
These two starting hands are the major players in hold’em. It’s not often you’ll get dealt Aces or Kings. In fact you get either Aces or Kings once in every 110 hands, so it’s not nearly as often as we’d like. Aces are by far the best possible starting hand in hold’em, closely followed by Kings. However, you should be aware that even Aces or Kings can get cracked, and they don’t play too well against multiple opponents. This means you should definitely be raising pre-flop to narrow the field. Extra caution is necessary when playing Kings, because if an Ace falls on the flop then you’re losing to anyone who has a single Ace in their starting hand. While they are very strong hands which most players love to get, they are certainly not unbeatable.
Group 2: QQ, JJ, AKs
Queens and Jacks are great starting hands, and with either of these, you can usually be confident you have the best starting hand. Of course they are dominated by Aces and Kings, but they’re a favourite against all other starting hands. While Queens and Jacks will occasionally run into a player holding either Aces or Kings, it doesn’t happen too often. Play these cards strongly, and always look to raise with them.
Ace-King is known throughout the poker world as Big Slick, and when suited it’s often called Super Slick. While it isn’t a ‘made hand’, unlike a pair, it offers great potential. It’s only a big underdog to Aces and Kings, and even pairs like Queens and Jacks are only slight favourites. The beauty of AK (suited or unsuited), is that it dominates so many other hands like AQ, AJ, AT, and so on. These types of hands are the ones that players usually end up pushing all-in with late in a tournament.
Group 3: TT, AK, AQs, AJs, KQs
This next group of starting hands is also a strong bunch. You should definitely be looking to raise pre-flop with any of these hands too. We’ve already talked about the power of AK, but starting hands like AQs, and AJs, are also very strong and often run into weaker Ace-X combinations. Even though these are all strong starting hands, and most of the time you’ll be winning pre-flop, you have to be careful – particularly a hand like KQs, which you can easily fold to a re-raise.
Suited Cards
You’ll often hear novice players responding to questioning of why they played a particular starting hand with the line “well, because they were suited”. Some suited cards are worth playing and it’s certainly better to start with suited cards than unsuited cards. However, the odds of flopping a flush is 1 out of 118 hands (0.8%) with two suited cards, and you’ll only make a flush after the river around 6.5% of the time. Don’t fall into the trap of playing any two cards just because they happen to be suited – it doesn’t make a big enough difference to make junk hands valuable.
Kicker Issues
The word ‘kicker’ means the smaller of your two cards. Some players play a hand if it contains an Ace with any other card (such as an Ace with a 3 kicker), and this type of play ultimately cost players money and tournaments. For example, let’s suppose a player calls with A6 and the flop comes A83. What does the player do? bet? call? raise? call a big raise? go all-in? What if the flop comes Q63? The player has middle pair – which is very hard to play. Hey, the flop could come A6X – the player has two pair, Aces and sixes but this happens only 1 out of 49 hands (2%). Until you learn when and how to play Ace junk (AX) go slow with it. One good thing about A junk and K junk, is that you do not need to play these hands to learn when they may be profitable. Let experience from other hands and study be your teacher.
Table Conditions
Hold’em starting hands can be a complex subject because every situation is different. If you were to ask a professional poker player, “should I call, raise, or fold this hand pre-flop?” his response would almost certainly be “it depends!” Here are some of the main reasons why it depends:
The Number of Players
The value of certain starting hands is very dependent upon the number of players at the table. Certain starting hands are always going to be under threat against a table of nine or ten players, but the value of these same hands increases when there are fewer players. A starting hand like KJ might be vulnerable against a full table of players, but is considered a strong hand if there are just a few other players.
Position
Your position on the poker table will be a major factor in deciding which starting hands you should play. The later your position in the betting order, the better – because you get to decide what to do after most of your opponents have acted. We’ll talk much more about the importance of position throughout our lessons on Pokerology, but as a first step please see our lesson on the value of position. Playing position can elude us at first because it is a part of poker that lends itself to be exploited through experience. However, you must quickly realize that your position at the table should heavily influence the choice of starting hands that you play. Until a player has a feel or grasp for positional play, just believe and follow some of the suggestions on the subject.
A Raised Pot
Whether or not a pot has been raised should be a very important factor in your decision to play a particular starting hand. Your selection of starting hands should change when the pot has been raised by a reasonable player. If there has been a raise and a re-raise before you’re due to act, then you should only consider playing with a very strong hand. Of course this will also depend on the personality types of the other players and whether the game is very loose or passive.
Starting Hand Charts
When you first start playing poker it can be helpful to use a starting hand chart as a point of reference. We’ve created a couple of starting hand charts that can be used by beginners. Please click on the following links to view these charts (they will open in a new window):
Each of these charts loads as a PDF, meaning they be viewed on screen, bookmarked or better still, can be printed and studied offline.
Beginners can treat starting hand charts as the gospel, but once you know enough about the game to recognize appropriate opportunities, you can deviate because your adjustment may represent a more profitable play. Our starting hand charts are a guide, not a set of intractable rules. There is no such thing as a perfect starting hand chart, because every game is different and there are many variables at work. Game texture and table conditions can’t be measured and included into a neat formula.
There are many factors that may encourage you to tighten or loosen your play from our guidelines. If you have a starting hand that’s not listed on the chart, then there’s a good reason – it should almost always be mucked. But as in all poker decisions the phrase, “It depends” comes to mind. However, before you decide to deviate from our guidelines, have a reason for taking such an action.
Conclusion
Don’t fall into the trap of playing any two cards. Most poker players want to play hands and as a beginner it’s very easy to be seduced by suited cards or picture cards, or any two-card holding that contains an Ace of a King – but if you play hold’em correctly, you’re going to be selective and toss away the vast majority of hands you’re dealt.
When you gain more poker playing experience you can begin to open up your range of starting hands – but until then, proceed with caution and only play the best hands. Loose, promiscuous play will get you into trouble and is the downfall of many players.
In future lessons we’ll expand much more on the topics discussed in this poker lesson and get you to think beyond the actual cards you’re dealt. We also have hours of video footage covering starting hand selection for both no-limit and fixed-limit hold’em – so depending upon your preference, be sure to check them out!
Related Lessons
By David Sasseman
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/78432412-56a741f15f9b58b7d0e84d3a.jpg)
David lives in Atlanta, Georgia, and has played over a million hands online and many thousands of hands in Mississippi, Louisiana, Florida, Illinois, Indiana, and Las Vegas casinos.
Related Lessons
Related Lessons
Now that you understand the position concept we are going to expand on that by looking at the subject of which starting hands to play and which to throw in the muck.
Ranking Best Starting Poker Hands To The Worst Poker Hands
This is the area where inexperienced players become fish, simply by not having the ability to fold weak hands before the flop. You can save a lot of money at this stage of the hand just by simply choosing not to play.
The Importance of Starting Hand Selection
As you know Poker is a game of maths and probability. It is therefore possible to know which starting hands are most probable to win a hand and this has been statistically proven in many studies. These studies have been able to rank starting hands according to how likely they are to win the hand against a random selection of opponent’s starting hands.
Starting hand
By Starting Hand we mean the two hole cards which are dealt to you at the start of each hand.
Since we now know which are the best starting hands in poker then we can apply this knowledge to our strategy. Remember, when we play a hand, we want to play with the odds in our favour, and by selectively choosing which starting hands we play we can ensure this.
Of course if we just waited for the two or three best poker starting hands then we wouldn’t actually play many hands as the probability of these cards being dealt is only once in a while.
So we combine the position concept with our starting hand concept, to allow us to only play a narrow starting hand selection when out of position and to play a wider range of starting hands when we are in position. Therefore the benefit of playing in position makes up for the weaker starting hands we may play.
Starting Hand Groups
You could look at all the statistical information and studies, but we’ve taken all the work out of it for you. The following section is a key part of your strategy and you should practise choosing the right action before the flop using the poker starting hands chart below.
We have chosen 46 different hands that we will play depending on the position and situation we are in. Those 46 hands have been separated into 8 groups named Group A to H. Group A are the strongest hands in poker based on the statistics and group H are the weakest hands that we are willing to play. Of course there are many more hand combinations weaker than the hands in Group H, but we are not interested in playing with these and they will be folded into the muck straight away.
Group B
AK
Group D
AQs
AQ
AJs
99
88
Group F
AT
KQ
KJs
QJs
44
33
22
Group H
KJ
KT
QJ
J8s
T8s
87s
76s
The ‘s’ next to some of the hands stands for Suited, so two cards of the same suit. ‘AJs’ could stand for A J whereas ‘AJ’ could stand for A J
Take a minute just to browse the hands in each group, you don’t need to memorise these, as you can use the chart to refer to, and once you have used it for a while, you will start to remember which hands are in which groups.
Poker Starting Hand Charts
Ok, so now we have our selection of 46 hands, and have split them into 8 groups based on strength, now what? Well we won’t just automatically play any of those 46 hands when they are dealt to us, we will make a decision based on the position we are in, and the situation we are faced with at the table.
When we are in position we will play a wider range of groups and out of position we will only play the stronger groups. Similarly when opponents have shown strength at the table by raising we will only play the better cards against them.
There are three charts, UNRAISED, RAISED and BLINDS. These are our Action charts, and show us what action to take when we have a hand in one of the starting hand groups.
The three charts are:
- UNRAISED – When everybody acting before you has either folded or called the big blind.
- RAISED – When somebody acting before you has raised.
- BLINDS – When you are in either the small blind or the big blind position and somebody acting before you has raised
| UNRAISED | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Everybody acting before you has either Folded or Called the Big Blind | ||||
| Action | Early Position | Mid Position | Late Position | |
| Opening Raise | A B C D | A B C D E | A B C D E F | |
| Call a Re-Raise | B C | C | C D | |
| Raise a Re-Raise | A | A B | A B | |
| Call the Big Blind (if Multiway Pot) | F G | G H | ||
| RAISED | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Someone acting before you has Raised already | ||||
| Action | Early Position | Mid Position | Late Position | |
| Re-Raise | A B | A B | A B | |
| Call | C | C | C D | |
| BLINDS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| After a Raise and You are in the Blinds | ||||
| Action | Raised from Early Position | Raise from Mid Position | Raised from Late Position | |
| Unraised Blinds – Play as if you were in Late Position in the Unraised chart | ||||
| Re-Raise | A | A B C | A B C D | |
| Call | B C D | D E | E F | |
To use the charts, just follow these steps:
- What group is your starting hand in? if it isn’t in any group then you Fold.
- What Situation are you in? Choose one of the three action charts relevant to the situation you are in.
- What Position are you in? Look at the column in the chart for the position you are in.
- Starting Hand Group not shown? If your starting hand group is not shown in that column, then you Fold.
- Starting Hand Group Shown? If your starting hand group letter is shown then take the action the chart is showing you.
The different actions in each of the charts are:
- Opening Raise – Make the first Raise
- Call – Just Call when a person has Raised
- Re-Raise – Re-Raise a person who has Raised
- Call a Re-Raise – Call when someone Re-Raises your original Raise
- Raise a Re-Raise – Re-Raise when somebody has Re-Raised your original Raise
- Call the Big Blind – Just call the big blind amount (also known as ‘limping in’)
Quick Reference
I don’t expect you to memorise all the starting hand groups and action charts. The way to learn them is by putting them into practise and then over time you will start to memorise them. But to start with, you can refer to the charts while you are playing.
You can either just bookmark and pull this page up each time you play or we have a couple of other methods to make your life a bit easier.
Printable Starting Hands Chart
A neat and tidy, A4 size starting hand chart which you can print and keep in front of you for quick reference while you are playing.
To download the Starting Hands Chart right click on the link and select save target as.
It is a PDF file, so to view and print this you will need the free Adobe Acrobat Reader. If you don’t have this you can download it here.
Starting Hands Chart Desktop Wallpaper
Use this as your computer desktop wallpaper. It is designed so that whilst you are playing poker, you can place your poker table window over the Poker Professor logo and all the charts will be visible around the table. Neat huh!
To download the Starting Hands Wallpaper right click on the link and select save target as.
To set as your desktop wallpaper, right click on the file you have just downloaded and select “Set As Desktop Background”.
The wallpaper is optimised for a desktop screen size of 1920×1080 as this is the most common. It should work with most other desktop sizes as well as windows should automatically resize it for you.
Starting Hand Examples
Lets take a look at some example starting hands and walk through what the charts are telling you to do and what thought process to follow.
Example Hand 1
You are sitting in early position and are dealt A J. You are first to act and so nobody has bet before you.
- What group is my hand in – AJ is a Group E hand
- What situation am I in – Nobody has raised before me so UNRAISED
- What position am I in – Early Position
So from the answers to the above questions we look at the UNRAISED Action chart, and look in the column for Early Position. You will see that Group E is not shown in that column so we are not allowed to play a Group E hand in Early position in this situation and so we would fold this hand.
Example Hand 2
You are sitting in early position and are dealt A K. You are first to act and so nobody has bet before you.
- What group is my hand in – AK is a Group B hand
- What situation am I in – I am first to act so it is UNRAISED
- What position am I in – Early Position

So from the above we look at the UNRAISED Action chart, and look in the column for Early Position. You will see that with a group B hand we are told to make an opening raise. So we would enter the hand by making a Raise (We will look at details of how much to raise later in the lesson).
Example Hand 3
You are sitting in Mid Position and are dealt A A. A Player in early position has raised the pot up to 3 times the Big Blind.
- What group is my hand in – AA is the best starting hand and therefore a Group A hand
- What situation am I in – There has been a raise by a player in early position, so it has been RAISED
- What position am I in – Mid Position
So, we look at the RAISED Action chart, and look in the column for Mid Position. You will see that with a group A hand we are told to make a Re-Raise. So we would enter the hand by making a Re-Raise. (We will look at details of how much to raise later in the lesson)
Example Hand 4
You are sitting in Mid Position and are dealt 9 9. A Player in early position has raised the pot up to 3 times the Big Blind.
- What group is my hand in – 99 is a Group D hand
- What situation am I in – There has been a raise by a player in early position, so it has been RAISED
- What position am I in – Mid Position
So, again we look at the RAISED Action chart, and look in the column for Mid Position. You will see that we are not allowed to play an already RAISED pot in Mid Position with a group D hand. So we fold this hand.
Example Hand 5
You are sitting in Late Position and are dealt 8 7. Two Players acting before you have limped in and called the big blind.
- What group is my hand in – 87s is a Group H hand
- What situation am I in – There has been two limpers, but no raise, so it is UNRAISED
- What position am I in – Late Position
So, we look at the UNRAISED Action chart, and look in the column for Late Position. You will see that we are allowed to Call a Multi-way pot with a group H hand (multiple players playing the hand). As two people have already called and the blinds will likely also call we can call the big blind and play the hand. So we would call the big blind on this hand.
Rank Of Poker Hands
How much should I Raise?
An opening Raise in general should be between 3 to 4 times the Big Blind. Anywhere in this range is ok, and as guide to start with I would raise the following amounts:
- When you are in EARLY POSITION Raise 4 times the Big Blind
- When you are in MID POSITION Raise 3.5 times the Big Blind
- When you are in LATE POSITION Raise 3 times the Big Blind
You should mix and match the size of your raises to prevent your opponents getting a read on your betting patterns, but the above can act as a general guide whilst you get used to your new strategy.
The reason to Raise more in Early position is because we are out of position and want to put as much pressure on our opponents as we can.
How much should I Re-Raise?
Best Starting Poker Hands Hold'em
A Re-Raise should in general be between 2 – 4 times the original Raise, As a guide:
Ranking Best Starting Poker Hands Texas Hold Em
- When it has been Raised from EARLY POSITION Raise 2 times the Raise
- When it has been Raised from MID POSITION Raise 3 times the Raise
- When it has been Raised from LATE POSITION Raise 4 times the Raise
The reason for this is it is more likely that a player in late position has raised with a weaker hand than a player in Early position.
Poker Starting Hand Chart
Practise Time
Well, that was a lengthy lesson and a lot to take in. Don’t worry, with practise it will start to become second nature, and that is exactly what you should do now with the first stage of your bankroll challenge.
Poker Bankroll Challenge: Stage 1
- Stakes: $0.02/$0.04
- Buy In: $3 (75 x BB)
- Starting Bankroll: $25
- Target: $3 (1 x Buy In)
- Finishing Bankroll: $28
- Estimated Sessions: 1
Use this exercise to get used to selecting which starting hands to play and which not to play according to the Starting Hands chart and get used to understanding what position you are in at the table. Don’t get too carried away at this stage though, play conservatively and be aware that someone may have a better hand than you. We are going to learn in more detail about betting after the flop later in the course.